Wetting
The Physics Behind Wetting
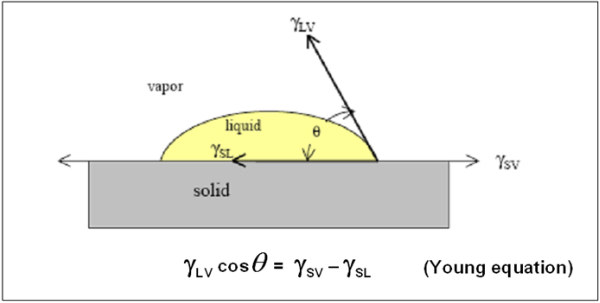
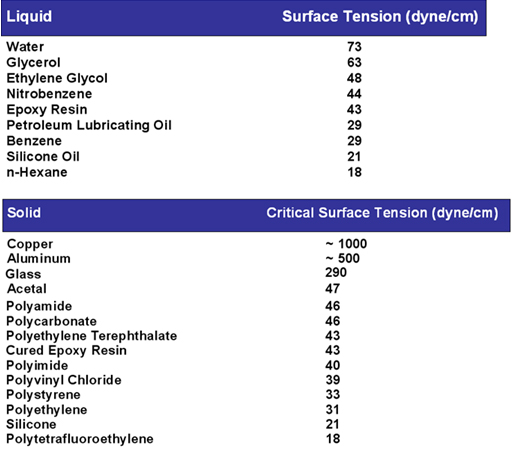
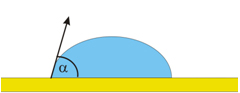
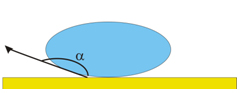
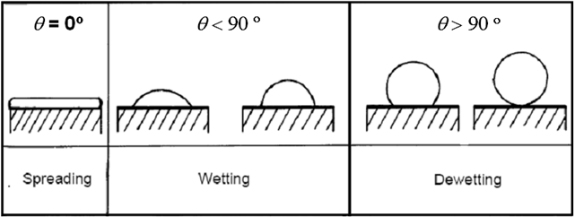
Wetting is the ability of liquids to form interfaces with solid surfaces. To determine the degree of wetting, the contact angle (q) that is formed between the liquid and the solid surface is measured. The smaller the contact angle and the smaller the surface tension, the greater the degree of wetting.
WETTING
Adhesion Forces > Cohesive Forces
Spreading of the liquid on the surface of the solid.
Contact Angle q : 0 < q < p/2
DEWETTING
Adhesion Forces < Cohesive Forces
The liquid pulls itself together into the shape of a droplet.
Contact Angle q : p/2 <q < p

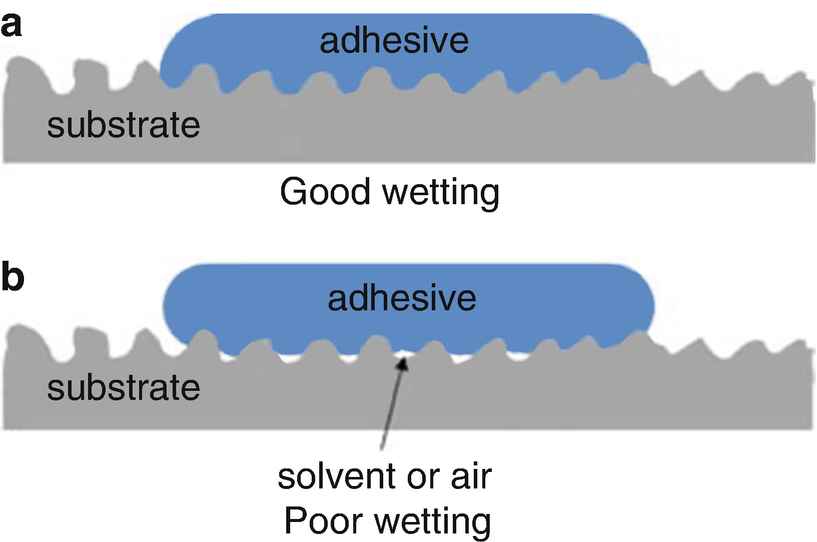
Spreading
For maximum adhesion the adhesive must completely cover the substrate, i.e. spreading is necessary.
The contact angle is a good indicator of adhesive behavior.
Contact Angle & Surface Tension

Rheology
Rheology falls under the broader subject of mechanics. It concerns how a body (solid, liquid or gas) is deformed on being exposed to external forces. Ideal fluids such as liquids or gases undergo irreversible deformation – they flow. Solids can also be irreversibly deformed if they are subjected to sufficiently large forces – and in that case they also flow.
In addition to the force, the time factor must also be taken into account here.
The following example will demonstrate this relationship:
The glass in the famous windows of Chartres Cathedral in France has “flowed” since these windows were made more than 600 years ago.

In the Middle Ages, the glass panes that were fitted were equally thick at the top and bottom edges. However, over the course of time the silicates have flowed downwards under gravity to such an extent that the thickness of the individual panes of glass at the top has become wafer thin. At the bottom, the thickness of the glass has almost doubled. Solid glass can therefore be considered a fluid – but one must wait a long time to see it flow!

Viscosity
Of critical importance for the viscosity of an adhesive is the molecular structure, especially the length of the main chains and the presence of any side chains, and the presence of polar groups. The latter are largely responsible for the forces that affect the mobility of the side-groups and chain segments.
Examples of typical viscosity levels:
| Petrol | 0.65 |
| Water | 1.0 |
| Mercury | 1.5 |
| Grape Juice | 2-5 |
| Blood (at 37 deg C) | 4-25 |
| PetrolP | 0.65 |
| Coffee Cream | ~ 10 |
| Honey | ~104 |
| Polymer Melts | ~ 103 – 104 |
| Bitumen | ~ 108 |
| Glass | ~1023 |
(h in mPa s at 20 deg C)
High viscosities are advantageous in order for example to avoid too much running of the adhesive at the edges of the bonded joints. Different viscosities are required depending on the intended method of application: for example, low viscosities are required for spraying and a paste-like material for application by screen printing. The viscosity can be increased to the desired application viscosity by adding thickening agents, e.g. silica gels. If the viscosity of solvent-based adhesives is too high, then more solvent can be added.
The viscosity of solvent-free adhesives can be changed very little by the user; however the viscosity can be altered in adhesive systems that already contain reactive thinner in their formulation.
The viscosity of an adhesive (h) is given as a value for the dynamic viscosity in Pa s; this is given in mPa s for adhesives of low viscosity.
It is defined as the force in newtons that is necessary to move one boundary surface parallel to the opposite surface in a fluid layer of 1 m2 surface area and 1 meter height at a speed of 1 meter/second. This measured with viscometers or rheometers that are constructed according to the nature of the flow processes being investigated.
Thixotropy is the property of a fluid material to temporarily transform into a state of lower viscosity as a result of the action of mechanical forces (e.g. stirring, shaking, kneading). Thixotropic adhesives are formulated in a customized way whereby thixotropic agents, e.g. silicic acid compounds, are added to formulations.
This confers the following benefits on the adhesive:
- No running on vertical bonding areas;
- No or very little absorption of the adhesive by porous substrate materials; improved application and coverage of the adhesive;
- Higher adhesive film thicknesses can be achieved.